When behavior problems arise, your vet may recommend drug therapy and environmental changes for your cat. These interventions work best when coordinated with a behavior modification plan.
What is behavior modification? What does behavior modification for cats involve?
behavior modification for cats – more than just training and medication
Behavior modification is a type of behavior therapy. It has its roots in the work of B. F. Skinner in the 1930’s. Skinner was psychologist who believed behavior is a response to an organism’s environment and is not a consequence of mental states (beliefs, memories, desires, plans) (Reference 1).
Skinner came up with the theory of operant conditioning. In operant conditioning, reinforcement and punishment are used to encourage or discourage behaviors (Reference 2).
Reinforce the Behavior – Make It Happen Again!
| Add Something “Good” | Take Away Something “Bad” |
| If you reward your cat for sitting with his favorite treat, he is more likely to sit the next time you ask. | If you stop trimming your cat’s nails every time she growls or hisses, you are reinforcing her behavior of hissing and growling at nail trims by “removing” the unpleasant nail trim. |
Punish the Behavior – Make It Stop Happening
| Add Something “Unpleasant” | Take Away Something “Good” |
| If you spray your cat with water when she jumps on the counter, she may be less likely to jump up on the counter. | Your cat claws at your hand for a treat. If you put the treat behind your back, the cat learns that the treat goes away when she swats at your hand. |
Operant conditioning forms the basis of many training methods. It appears to be pretty straight-forward: can we just reward the cat for using the litter box and spray her with water if she doesn’t?
Problem behaviors involve more than just a stimulus and a conditioned response. Operant conditioning does not take into account the emotional state of an animal. It may be difficult to positively reinforce or punish an animal that is fearful.
To modify or change problem behaviors, the animal’s emotional state must be addressed. Teaching a cat or dog a substitute behavior for the undesired behavior or medicating him does not teach him how to respond to other stressful situations in his life.
Christine Calder, a member the American College of Veterinary Behaviorists, describes a five step process in working with problem behaviors in dogs (Reference 3).
- Avoid all the things that cause the behavior.
- Open the lines of the communication – learn body language; stop punishment.
- Build a toolbox of known behaviors such as voluntary eye contact, touch, or a chin rest.
- Teach the animal to relax.
- Systematic desensitization and Counter Conditioning (to what triggers the behavior).
Behavior modification for cats can follow this five-step plan.
You may have gotten a new dog or your young nephew comes to stay with you. Your cat finds these new additions terrifying so she hides under the bed to be safe. She does not use her litter box because she is afraid the dog or the child will be there. You try to adapt the environment to accommodate your cat and the newcomers but your cat remains fearful.
Behavior Modification for Cats- More Than Just Training and Medication
- Avoid Triggers: We offer the kitty the sanctuary of a room or place in the house off-limits to the dog or child. This area has all the cat’s resources: litter box, cat tree, food and water.
- Establishing communication: Spend time with your cat, coaxing her to come to you; brush or pet her if she likes it. Learn her body language so that you know when she is done interacting (see “How to interact with your cat” ). Have your nephew also learn cat body language. Stop punishment: no spraying with water bottles; speak to your cat quietly with a pleasant tone.
- Toolbox of known behaviors: For a cat, these may be targeting on your finger or a stick, and learning to pay attention to you through eye contact.
- Teach the cat to relax: A cat who is relaxed is calm. She is able to devote more of her energy to learn how to cope with new situations. When the cat can relax on cue, she is able to choose a calm state. We can work up to asking for calm behavior when the dog or child is nearby.
- Desensitization: In this case, we introduce the cat to the dog or child in a safe situation. The dog or child is separated from the cat (use a barricade as needed) and the cat can come or go as she pleases. Gradually the distance between the cat and the dog or child is decreased.
- Counter-Conditioning: Previously, the cat associated the dog or child with being anxious or fearful. If she can be calm when dog is on the other side of the barricade, we can start to form some new associations using high-value treats or other things the cat likes, such as being brushed. With supervision, your nephew may be able offer your cat treats or brush her.
Behavior modification for cats is more than just substituting a desirable behavior in place of a problem behavior. For the intervention to work, the emotional state of the cat has to be considered. We need to give the cat a break from the stressful situation, then establish communication with cat. We need the cat to trust us and look to us for guidance. Teaching the cat to relax and getting accustomed to what triggered the behavior are the final steps of the behavior modification plan. The services of a cat behavior professional can be helpful in these situations.
references
- B.F. Skinner (1904-1990) Advocacy of Behaviorism and its Application to Psychology and Life
Operant Conditioning and the Law of Effect. https://psychology.fas.harvard.edu/people/b-f-skinner Viewed 5/2024. - Cherry, Kendra. What is Operant Conditioning? February 24, 2023. https://www.verywellmind.com/operant-conditioning-a2-2794863 Viewed 5/2024.
- Calder, Christine D. Behavior Modification for Dogs. Behavior Bytes. December 28, 2022. https://cattledogpublishing.com/blog/behavior-modification-for-dogs/ Viewed 5/2024.
Want to keep up with the world of cats? Subscribe to The Feline Purrspective!
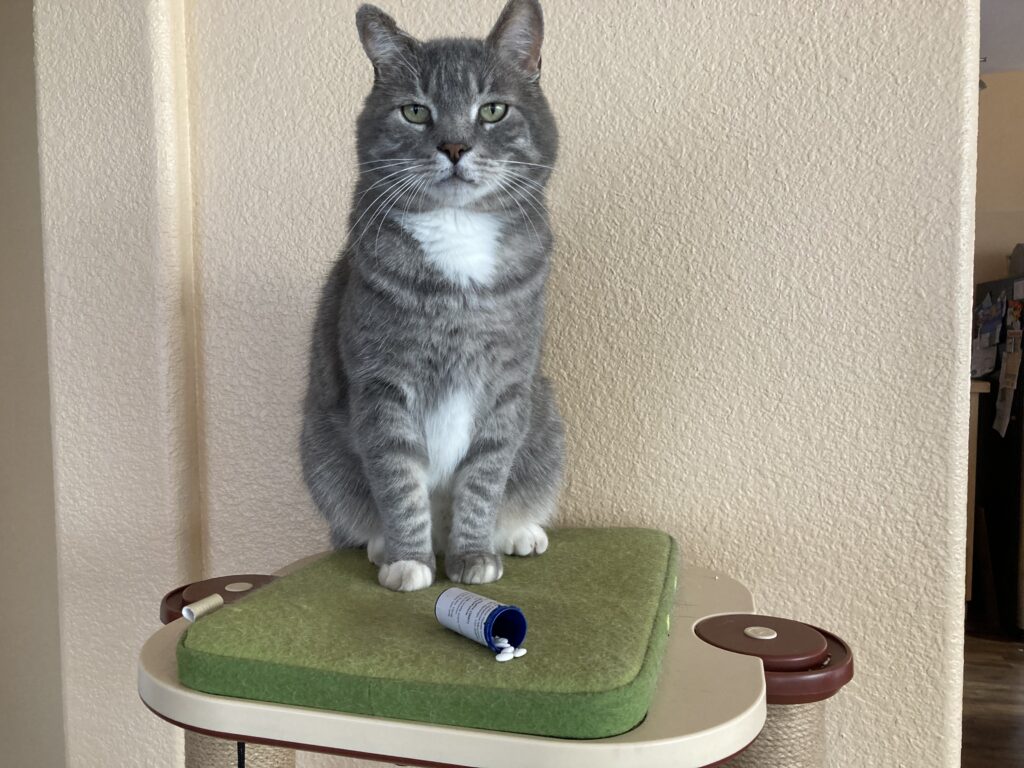
 Sometimes, fear and anxiety can make it difficult for a cat to cope with her daily life. Perhaps there has been a change in the environment – a new cat or dog comes to live in the home or a new born baby comes home one day.
Sometimes, fear and anxiety can make it difficult for a cat to cope with her daily life. Perhaps there has been a change in the environment – a new cat or dog comes to live in the home or a new born baby comes home one day.