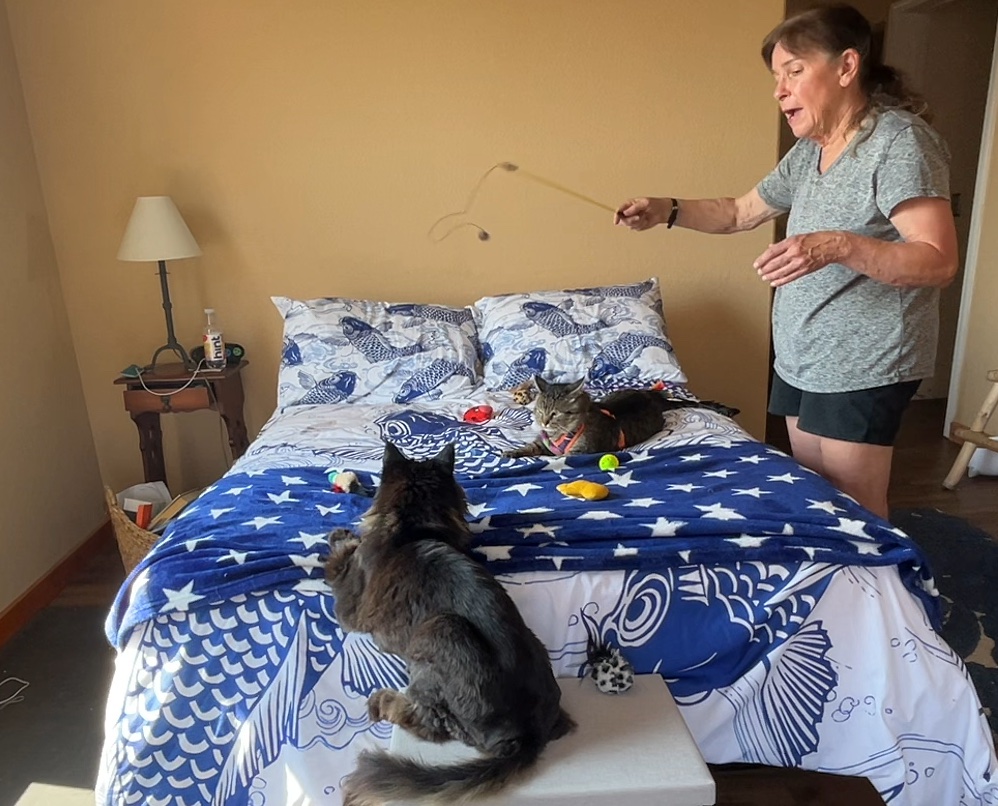
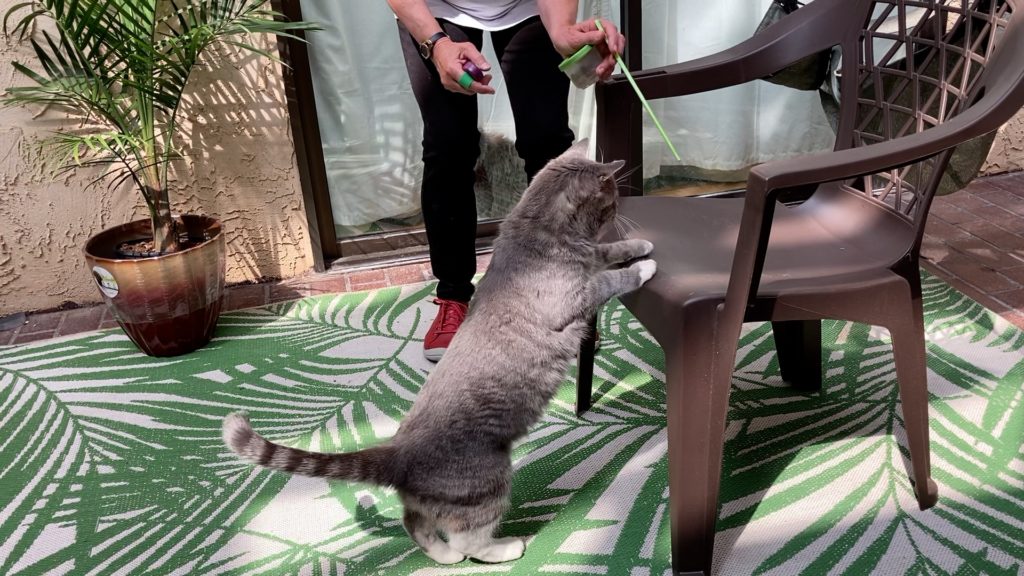
Your cats seem on edge lately. There is more hissing and growling going on. Two of your cats used to snuggle together and that has stopped. You have been finding tufts of fur in the hallway. These are signs that all is not well in your feline household.
If conflict between your cats is severe, a visit to your veterinarian to identify health and behavioral problems is in order. He or she may refer you to a veterinary behaviorist if:
- if there is active physical fighting going on
- there has been injury to other cats, pets or humans
- fear/anxiety leads a cat to not use the litter box
- a cat is hiding more than 50% of the time
In these cases, separation followed by a gradual reintroduction is recommended. But what about the situations that are not so bad? There is conflict but it is mild. No one has been hurt and all the cats are eating and using the litter box normally. Careful assessment of the environment and making some changes (more cat trees, feeding cats separately…) can help restore harmony (Reference 1). Another way you can encourage cats to tolerate each other is to use Group Behavior Sessions to manage conflict between cats.
Use Group Behavior Sessions to Manage Conflict Between Cats
Group behavior sessions feature playtime and other interactions between the owner(s) and resident cats. The goal of these sessions is to teach the cats that they can be calm (not aroused) when the other cat(s) are around. Toys and treats help cats make positive associations with the presence of the other cats. The presence of the owner(s) can help make a cat feel secure when the other cats are close by.
Group Behavior Sessions (reference 1)
- part of the daily/weekly routine
- all cats in the household can choose to take part in these sessions if they are comfortable
- sessions should be short (5-20 minutes)
Where should I do Group Behavior Sessions?
These sessions can take place in different areas in the house. Start with those areas that are “calmer”, where there has not been an instance of tension/conflict. Work up to “problem areas”, say where an outdoor cat came to the window, after successful sessions in the “calm” places.
What do I need for a Group Behavior Session?
- Have a variety of toys ranging from interactive toys to electronic and stuffed toys. It would be wise to avoid catnip toys as some cats can get pretty “wound up” with these.
- Treats can be useful to get the group together and to end the session on a positive note. These should be treats that are not available at other times.
- You may want to make sure there are some cat trees or boxes in the session environment for cats who prefer to observe and not play.
- Make sure to have some pillows or a sheet of cardboard to intervene if a cat becomes aroused (see Managing the Indoor Cat Fight).
What is my role in the group session? (Reference 1)
- Start the session by scattering a variety of toys around.
- Call the cats – you may need to lure them to the area with some treats.
- It is important to actively interact with each cat, one at a time, using toys or grooming them.
- If your cats have been trained to relax on a blanket or mat, have some of these around – you can offer cats who prefer not to play a massage (see Touch Can Relax Your Cat and Reduce Anxiety)
- Be sure to monitor each cat’s body language (see Touch Not the Cat). Be prepared to separate cats and end the session if tensions are on the rise (see Managing the Indoor Cat Fight).
- End the session on a positive note with some treats. Offer treats to each of the cats individually – be calm and don’t toss these; avoid having a more boisterous cat “steal” treats from a more timid cat.
A variety of things can trigger conflict in a multi-cat home. In the event that aggression is mild and cats don’t require separation, you can use group behavior sessions to manage conflict between cats. These owner-supervised play and interaction sessions help cats associate good things with their roommates and learn to be calm when they are together.
references
- Rodan I, Ramos D, Carney H, et al. 2024 AAFP intercat tension guidelines: recognition, prevention and management. Journal of Feline Medicine and Surgery. 2024;26(7). doi:10.1177/1098612X241263465
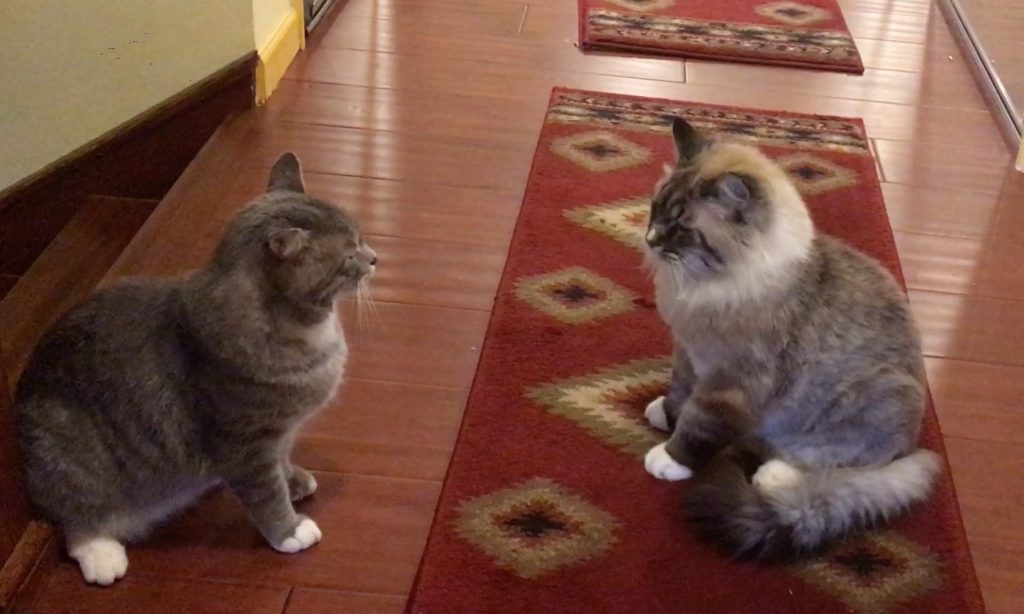
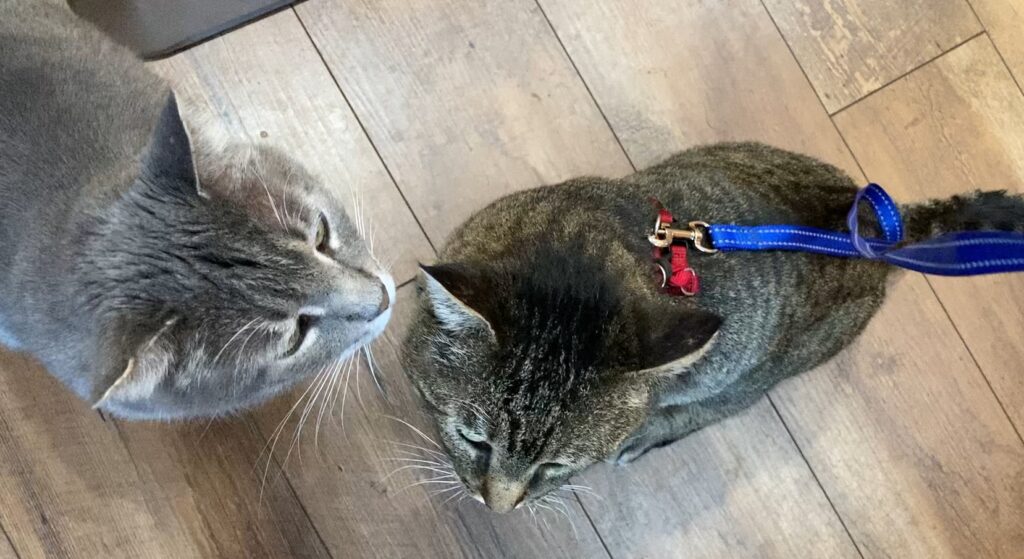
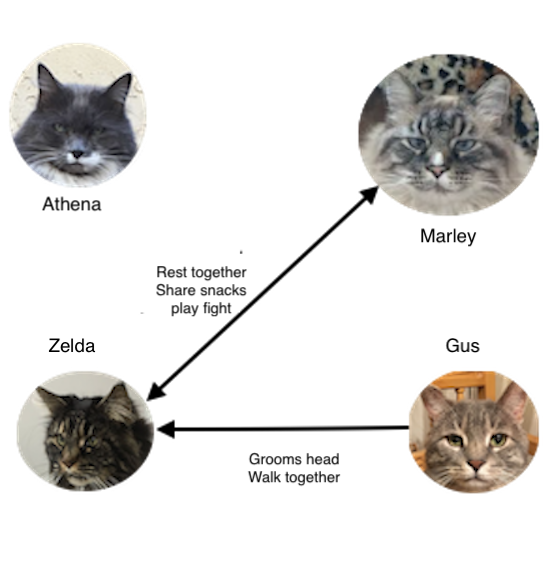
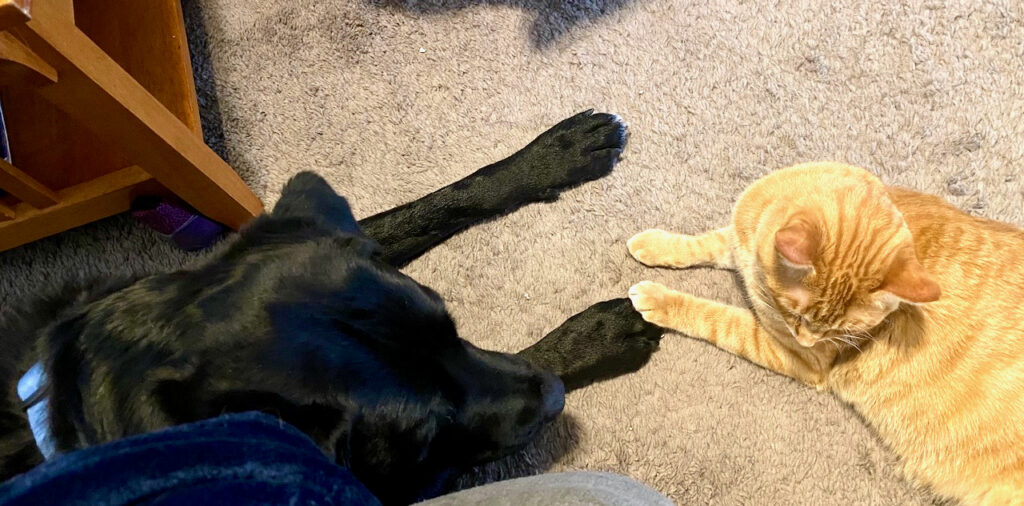








 In this post, we look at how cats get along with other species – are their behaviors affiliative or is there conflict?
In this post, we look at how cats get along with other species – are their behaviors affiliative or is there conflict? Cats use the same friendly behaviors when interacting with people as they do with other cats.
Cats use the same friendly behaviors when interacting with people as they do with other cats. A Tale of Tails
A Tale of Tails Do cats have personalities? If you
Do cats have personalities? If you 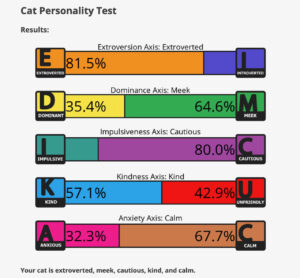






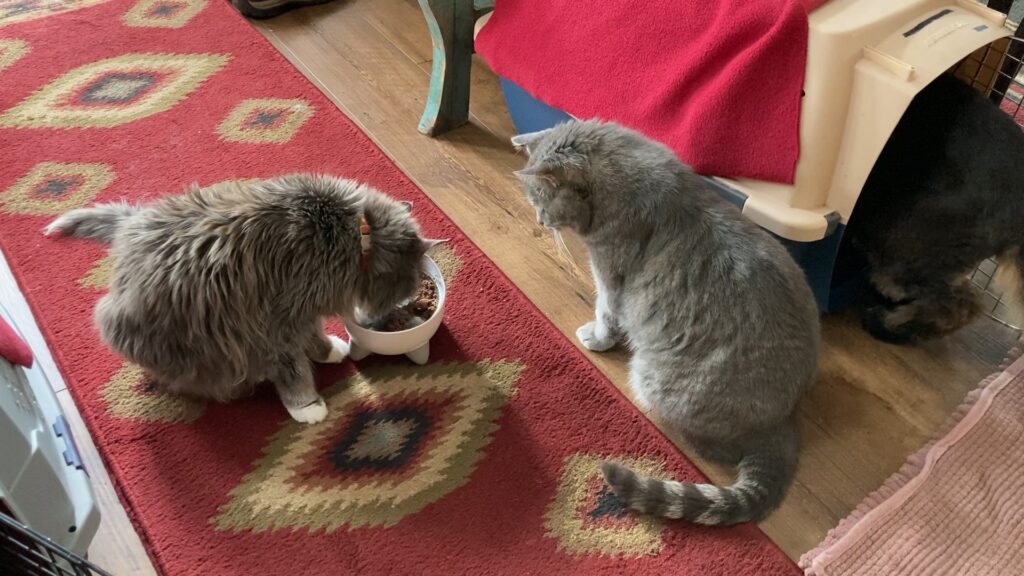
 Cats don’t have to be “preferred associates” to choose a spot in the sun in the same room as a housemate cat. As long as there is plenty of space, peaceful coexistence should be possible.
Cats don’t have to be “preferred associates” to choose a spot in the sun in the same room as a housemate cat. As long as there is plenty of space, peaceful coexistence should be possible.




