You’ve brought your senior cat in for her regular checkup and the technician asks you if you would like to have her blood pressure checked. Although your blood pressure is routinely checked when you go to the doctor, it has not occurred to you to ask to have your cat’s blood pressure checked. Should you have your cat’s blood pressure measured? How is it done – will it be uncomfortable? Frightening?
Why measure your cat’s blood pressure
As cats age, many develop hyperthyroidism and kidney disease. Other cats may develop diabetes. All of these conditions can result in the heart pumping harder to compensate for the changes. As the heart pumps harder, blood pressure increases and arteries, the eyes, the kidneys, the brain and heart can be damaged.
Left untreated, high blood pressure can result in:
- blindness
- increasing loss of protein through the kidneys >> shortened life span
- disorientation, lack of balance, seizures, altered mentation or behavior, or weakness in the limbs
The best way to avoid these consequences is to monitor your cat’s blood pressure and start treatment if his blood pressure is high.
So how do we measure your cat’s blood pressure?
When measuring blood pressure in humans, we typically place a pressure cuff on the upper arm, inflate the cuff until the flow of blood to the artery is shut off . The cuff is then released, and a wave of blood fills the artery, turbulent at first, then subsiding to a smooth flow.
The human practitioner can use a stethoscope to listen to the sounds made as the blood rushes back into the artery.
- The first sound is heard at the systolic blood pressure (the higher number in 120/80)
- The final sound is heard at the diastolic pressure (the lower number in 120/80).
We will also use a blood pressure cuff to measure your cat’s blood pressure. This cuff can be put:
- on the front leg
- on the hind limb, above or below the hock (ankle)
- on the tail
Cats’ arteries are much smaller than humans’ and it is difficult to hear the sounds of the blood flow using a stethoscope, so we turn to other methods: Doppler and oscillometric.
Doppler
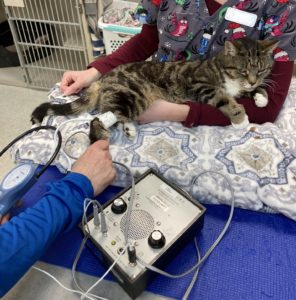
A Doppler unit measures blood flow.
- After placing the cuff on your cat, the Doppler sensor is placed over the target artery.
- Piezoelectric crystals in the sensor detect changes in the flow of blood in the arteries and convert these to sound.
- Acoustic gel on the sensor ensures good contact so that the practitioner can hear the heartbeat.
- The cuff is inflated until the heartbeat is no longer heard.
- The cuff is then released and the pressure at which the heartbeat can be heard again is the systolic blood pressure.
- Headphones are usually used when measuring blood pressure with a Doppler.
Doppler units give us a measurement of the systolic blood pressure, the larger number in the 120/80.
Oscillometric
Only a cuff needs to be placed to measure your cat’s blood pressure with an oscillometric unit.
- A sensor in the cuff detects the pressure pulses in the artery.
- As the cuff is inflated, the pulses decrease as flow to the artery is cut off.
- The cuff is then deflated and the pressure wave that results as the blood rushes back into the artery is analyzed.
Oscillometric units typically only measure the peak of this wave, the average blood pressure, and calculate the systolic and diastolic pressures.
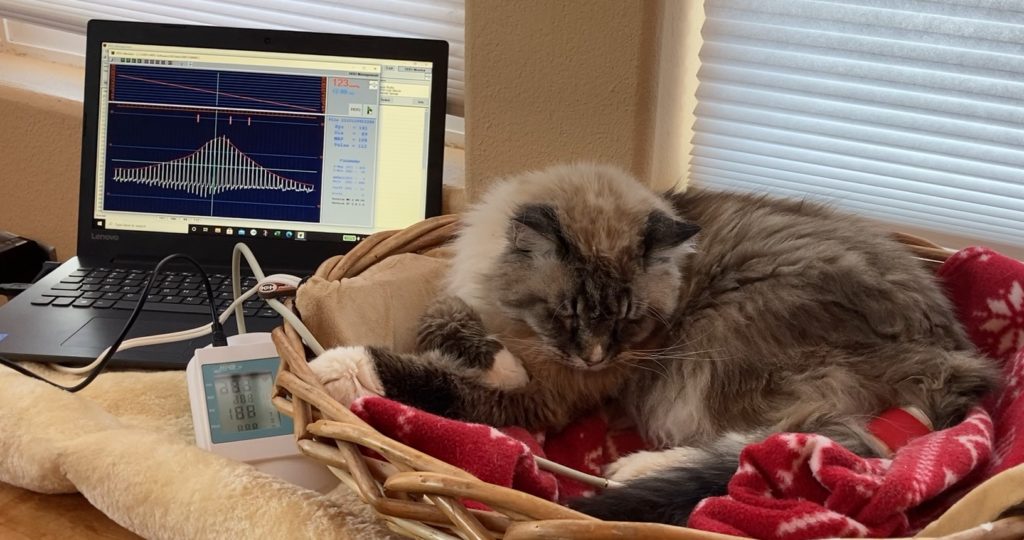
A High Definition Oscillometric unit records the entire pressure wave, directly measuring the systolic and diastolic pressures. An HDO unit is usually connected to a computer to view the pressure wave and determine if the measurement was accurate.
How accurate is a blood pressure if my cat is nervous at the vet clinic?
Just like people, cats get anxious and nervous when visiting the vet clinic. Blood pressure is sensitive to this and it can be a challenge to measure your cat’s blood pressure.
Putting the odds in our favor:
- Most of the time, you should be with your cat during a blood pressure measurement. Your cat knows you and trusts you. Your presence is reassuring and calming.
- Allow your cat to settle in for 5-10 minutes – the measurement should be done in a quiet room.
- If your cat likes to snuggle in your lap, see if the measurement can be done there. If your cat prefers to sit on his stomach, perhaps a tail measurement is best. If he is comfortable laying on his side, a hind leg may be better.
- Using the front leg to measure blood pressure puts the practitioner in front of the cat; curious cats may want to take a nibble at the blood pressure cuff. I prefer that your cat be facing you, her person, who can reassure her. I feel the tail and hind leg work better.
- The artery being measured, tail or hind leg, should be at the same level as the heart – so kitty should not be sitting up, but laying comfortably on his stomach or side.
What do the numbers mean?
- Again, like people, the systolic pressure is ideally around 120.
- Pressures 150 and over can indicate the need for medication.
- Your vet may also do an eye exam, looking at the eye with an ophthalmoscope or lens. In some instances of high blood pressure, the vessels in the eye dilate and become twisted; sometimes the retina may be detached, resulting in blindness. If high blood pressure is caught early enough, blindness may resolve with treatment.
My cat’s blood pressure is high but her eyes looked OK. What next?
High blood pressure can be treated with drugs – the most common drug used is oral amlodipine. Amlodipine takes effect fairly quickly and a blood pressure can be repeated in about 10 days and the dose adjusted if needed.
Other medications such as benazepril or telmisartan may be used alongside or in place of amlodipine.
I don’t think the reading was accurate – my cat was too nervous
It is worth investing in a home blood pressure visit. A practitioner can come to your home and get a measurement where your cat feels safe and secure.
Measuring your cat’s blood pressure especially as she gets older will help keep her healthy and comfortable. Without treatment, high blood pressure can have serious side effects, including blindness, seizures, and cardiac damage.
Have your cat examined regularly by your veterinarian, as changes to the eyes or a heart murmur might warrant a blood pressure check.
Want to keep up with the world of cats? Subscribe to The Feline Purrspective!



 Indeed, we are more familiar with dogs’ body language than that of cats. People see dogs as more social than cats. Someone getting a puppy will plan to take it places, walk it and play with it.
Indeed, we are more familiar with dogs’ body language than that of cats. People see dogs as more social than cats. Someone getting a puppy will plan to take it places, walk it and play with it.