“Music has charms to soothe the savage beast” is actually a misquote of the poem, The Mourning Bride, by William Congreve in 1697. The word “beast” is commonly substituted for the original word “breast”. But perhaps Congreve actually meant “beast” – a similar reference to “savage beasts” and music is found earlier with the Roman poet Lucan, whose work was translated into English by Thomas May in the 1620’s.
“…Whose charming voice and matchless musick mov’d
The savage beasts, the stones, and senseless trees…”
Music can arouse strong emotions in people – it can help instill a martial spirit, make us happy but also make us melancholy and sad. It clearly effects our mood.
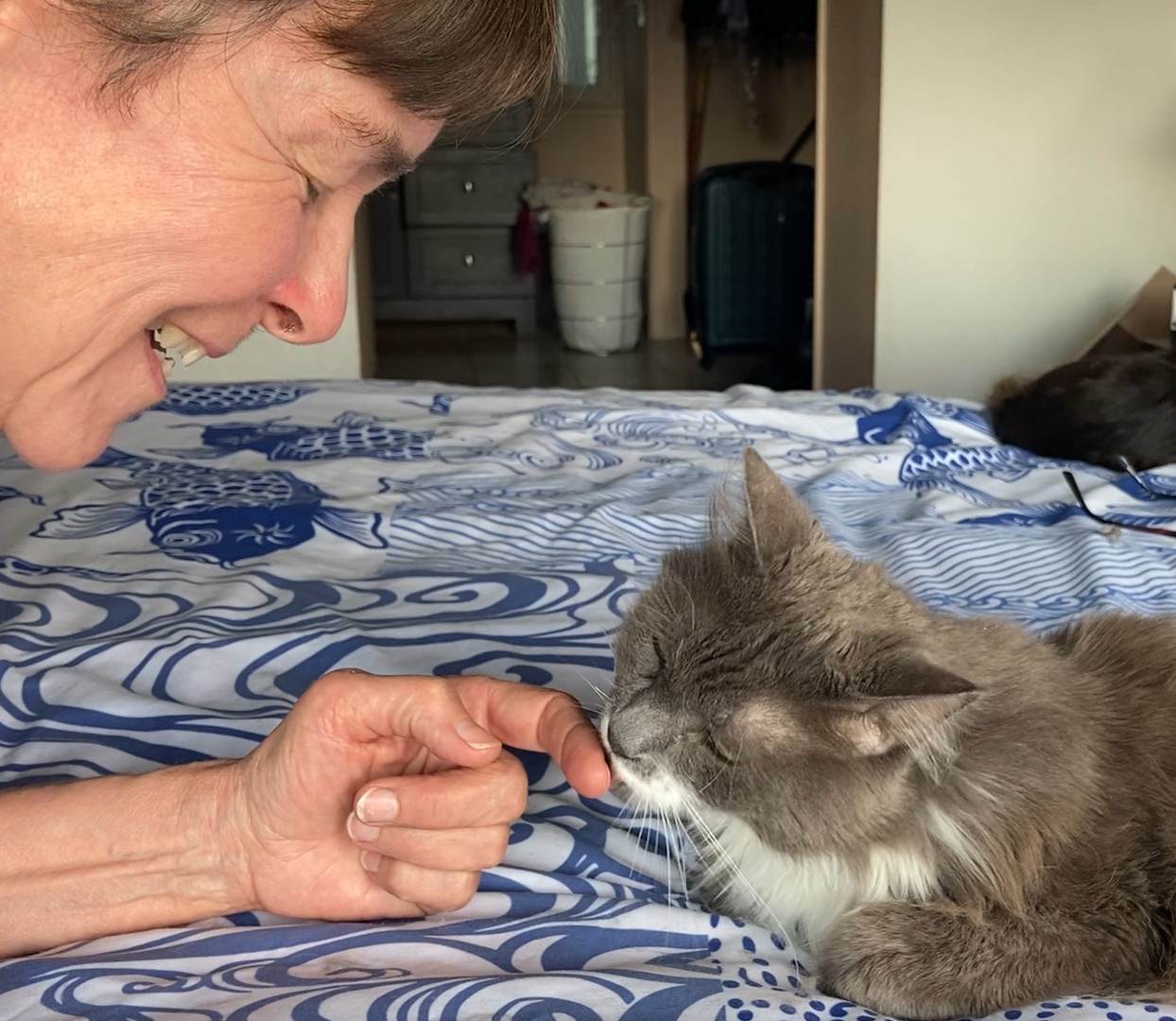
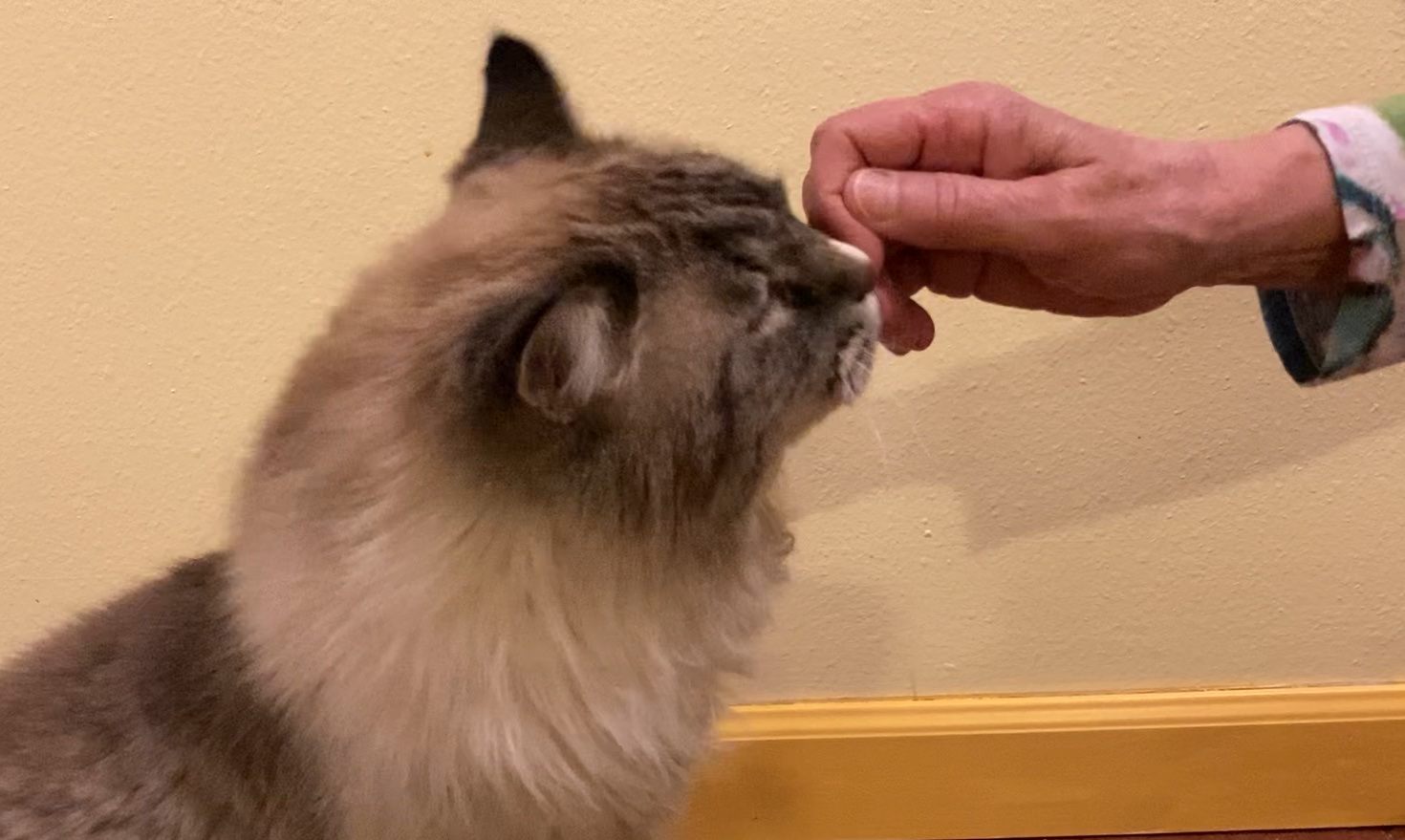
Researchers at the University of Wisconsin set out to find music that would affect the moods of our cats. Snowden, Teie and Savage created music for domestic cats that would calm the cats. They observed the responses of cats to the “cat music” and compared these with the cats’ responses to classical music that humans find calming.
Human Emotions and Features of Music
Specific features of music induce particular emotions in humans:
- Slow tempos, a narrow frequency range, decreases in pitch, longer sounding of the notes are characteristic of “sad” music
- “Joyful” music features fast tempos, increasing pitches and notes tend to be more staccato and not held very long.
- “Angry” music is louder and has a higher fundamental frequency; “fearful” music also has a higher fundamental frequency but notes are not held as long.
Snowden and Teie hypothesized that music with the features described above would affect cats in the same way as people, as long as the frequencies and tempos are the same as what is found in natural cat communication.
Cat Music vs Human Music
The “cat music” used in this study had an average pitch that was 2 octaves higher than the human music; it was also 1 octave higher than the fundamental frequency of natural cat communication (“meows” and “howls” were excluded).
The “cat music” also included elements at lower frequencies for the listening pleasure of the cats’ human friends. One piece contained a pulse rate of 1380 bpm, similar to purring, with melodic sliding frequencies; another had a pulse of 250 bpm, similar to kittens suckling, also with melodic sliding frequencies.
Do cats like cat music?
Snowden, Teie, and Savage’s study compared the reactions of 47 spayed and neutered cats to the “cat music” with the cats’ reactions to the human music. Researchers watched for the following responses:
orient/approach behavior
- orient head toward speaker playing music
- move toward speaker
- rub speaker
- purring
Avoid/fearful behavior
- leaving the room
- hair on end
- growling
- hissing
- arched back
results:
Cats showed more Orient/Approach responses to the cat music than the human music. They also approached the source of the cat music more quickly than the human music. There were few Avoidance/Fearful behaviors (9 out of 94 trials – same for both types of music).
Trying Out Cat Music
In 2019, the cat music was tested in the veterinary clinic at Louisiana State University. Twenty one cats completed the study. The cats presented for 3 examinations, two weeks apart. Each cat was exposed to one of three soundtracks : silence, cat music or classical human music. Each session included an examination and blood draw. The chosen soundtrack was played throughout the session, until the cat was placed back in her carrier.
Cat Stress Scores (CSS) were measured when the cat arrived, during the exam and at the completion of the blood sampling. A Handling Score (HS) was also measured during the examination.
The CSS and HS were not very different comparing cats exposed to silence and classical music; however, CSS and HS were significantly lower for cats exposed to the “cat music”.
cats prefer species specific music

Cat music can help reduce stress-related behaviors. I have found “cat music” useful to calm my kitties
- when work is being done on my house
- when I am transporting my cats in the car.
The cat music developed for the studies above can be purchased at https://www.musicforcats.com.
 You are sitting by the window, engrossed in your latest murder mystery. You don’t notice that neighborhood tabby outside your window but your cat does and goes into full battle mode, hissing and striking at the window. You look up and jump, as your cat turns and strikes out at you. She looks like a miniature saber tooth tiger! Alarmed, you throw your glass of water at her as you beat a hasty retreat.
You are sitting by the window, engrossed in your latest murder mystery. You don’t notice that neighborhood tabby outside your window but your cat does and goes into full battle mode, hissing and striking at the window. You look up and jump, as your cat turns and strikes out at you. She looks like a miniature saber tooth tiger! Alarmed, you throw your glass of water at her as you beat a hasty retreat. Why slide a block aside to uncover food when there is food freely available in a bowl nearby? Psychologists call the behavior “
Why slide a block aside to uncover food when there is food freely available in a bowl nearby? Psychologists call the behavior “

 Many of us (cat owners) dread taking our cat to the vet. There is the ordeal of the carrier and car trip; once there, your cat seems miserable. However, regular veterinary care is the key to a happy and longer life for your cat. Can medication before your cat’s vet visit help?
Many of us (cat owners) dread taking our cat to the vet. There is the ordeal of the carrier and car trip; once there, your cat seems miserable. However, regular veterinary care is the key to a happy and longer life for your cat. Can medication before your cat’s vet visit help?


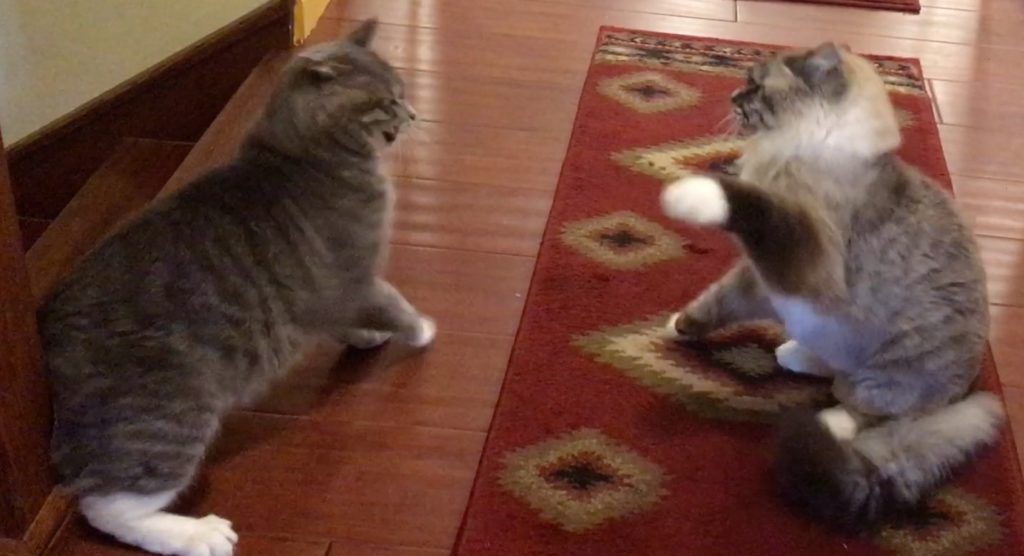
 Play usually ends with one cat standing facing the other cat, who may be on his/her side, or there is a chase sequence that just dies off, with the cats walking away from each other.
Play usually ends with one cat standing facing the other cat, who may be on his/her side, or there is a chase sequence that just dies off, with the cats walking away from each other.






